Aerobic Respiration in Plants
Aerobic Respiration in Plants: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Kreb's Cycle, Adenosine Triphosphate, Electron Transport Chain, Oxidative Phosphorylation, Aerobic Respiration, Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide, Cytochrome Oxidase and, ATP Synthase in Mitochondria
Important Questions on Aerobic Respiration in Plants
During glycolysis in cytoplasm, the decarboxylation reactions -----------------.
In ETS, ____ possesses the highest energy and ____ possesses the lowest energy.
How many molecules of last electron acceptor in ETS are required if one molecule of Isocitrate is a substrate during aerobic respiration?
Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
In which of the following biochemical reactions, is complex 'V' of ETS of the Krebs cycle not operative?
Study the given figure and select the incorrect option regarding this.
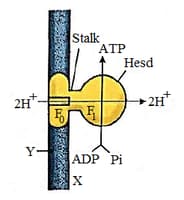
Decarboxylation is not needed in
Chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in the chloroplasts and mitochondria is based on
During ETC, how many ATP molecules will be synthesised when there is complete oxidation of molecules of ?
If we start with 2 molecules of glucose, the number of ATP at the end of aerobic respiration and number of pyruvate formed would be:
Number of molecules formed from one molecule of glucose is:
One of the common compounds in pathway and the Krebs cycle is:
During ETC, how many ATP molecules will be synthesised when there is complete oxidation of molecules of ?
Ubiquinone transfer electron to:
When two molecules of acetyl-CoA enter TCA, the net gain is:
Number of ATP formed per molecule of acetyl- is:
Ubiquinone provides it’s electron to
Mitochondrial inner membrane is permeable to NADH.
Shuttle system transfers electrons from the hydrogens of cytoplasmic NADH to the mitochondrial electron carriers across the mitochondrial membrane.
The electrons created during _____ are used for oxidative phosphorylation. (gluconeogenesis/ glycolysis)
